Commuting each morning via the 12km road tunnel during peak hours, it only takes a little more than 15 minutes to reach my destination from home. It is difficult to imagine thousands of cars passing through each day without hearing many accidents being reported on the news. However, when calamity arises, it is then clear that the safety systems have been put in place, ensuring the safety of road users at all times.
Have you ever wondered what is going on behind the scenes?
The road tunnels are designed in accordance with directives which specifying the minimum safety requirements. Aside from the emergency exits and emergency telephones available at regular intervals, it is paramount that the tunnels must always be supplied with power, light, fresh air and water for firefighting.


Take the ventilation system for example. It helps to remove toxic gases when the NOx, CO or CO2 levels are detected to be high during normal operations. In the case of a fire, the operator depends on the same system to purge the smoke and heat from the tunnel, away from motorists evacuating the tunnel or the emergency response team that is tackling the disaster.

To minimise potential casualties, Phoenix Contact has developed the Dynamic Evacuation Guidance (D.E.G). The automated D.E.G comprises of a full redundant configuration, where the guiding handrail is monitored by a pair of redundant PLC to guarantee maximum availability. Together with its 2-hour phosphorescence effect on the guiding handrail, the worst-case scenario during a loss of electrical power is also mitigated.
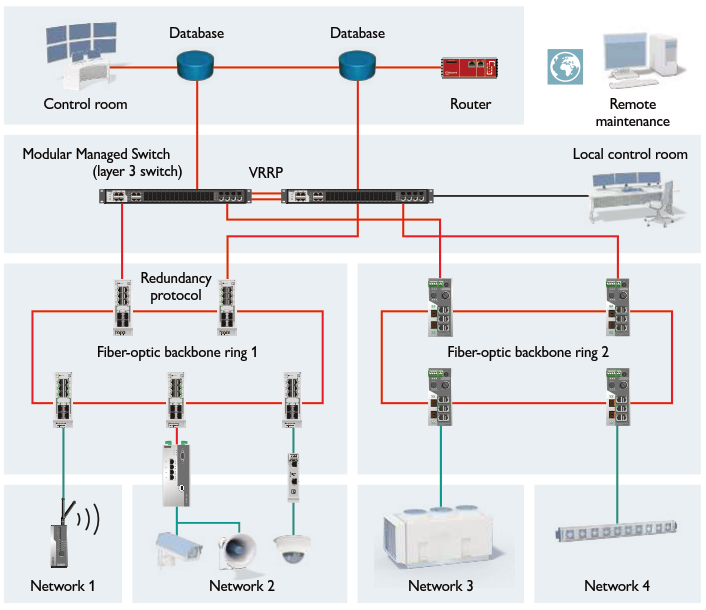
It is equally important to note that all state-of-the-art safety systems will not be operating at its best without a reliable communication network. The integrated backbone communication network is typically setup in several redundancy levels. At “switching level”, the entire tunnels are segregated into various “zones” covering certain sections of the tunnel. These “zones” are then grouped together through the “routing level”. With this structure, network failure (should it ever occur) can be isolated, without affecting other parts of the communication network.






 Are you selecting a safety relay just to meet the SIL3 requirements?
Are you selecting a safety relay just to meet the SIL3 requirements?

