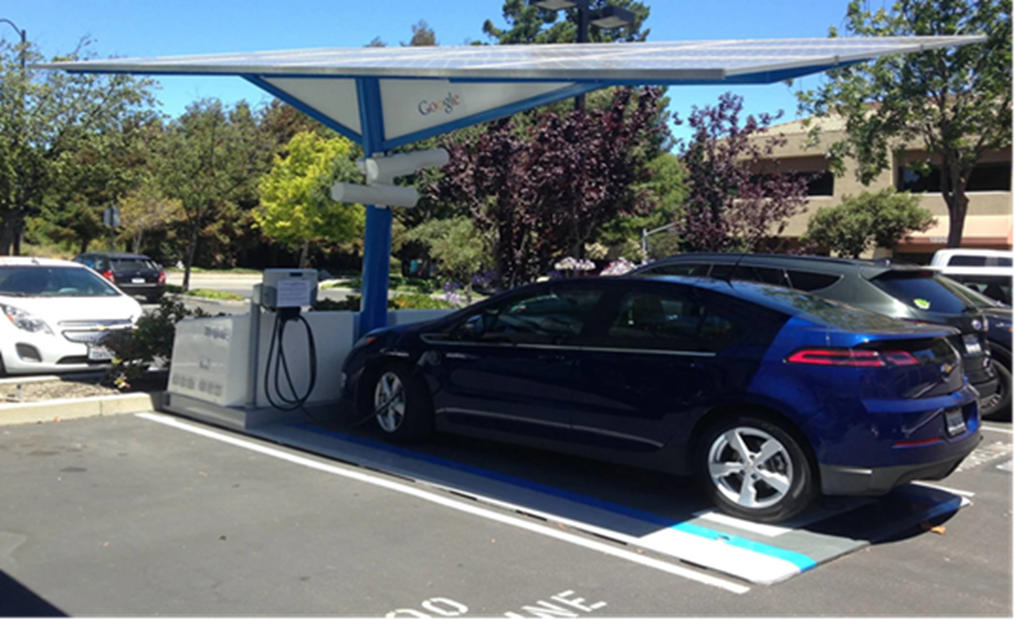
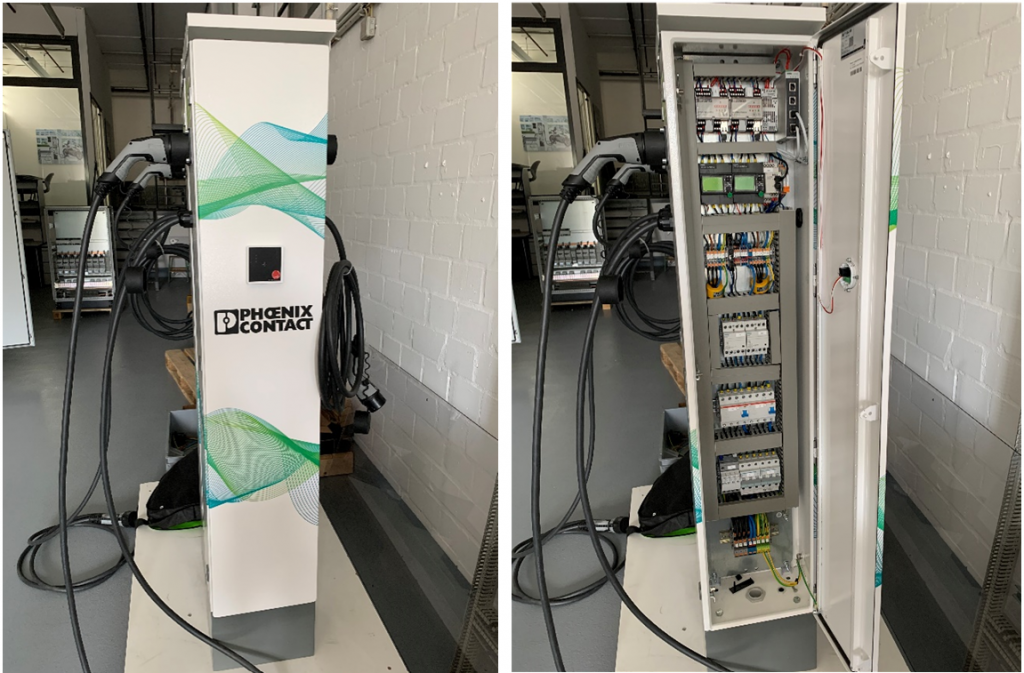
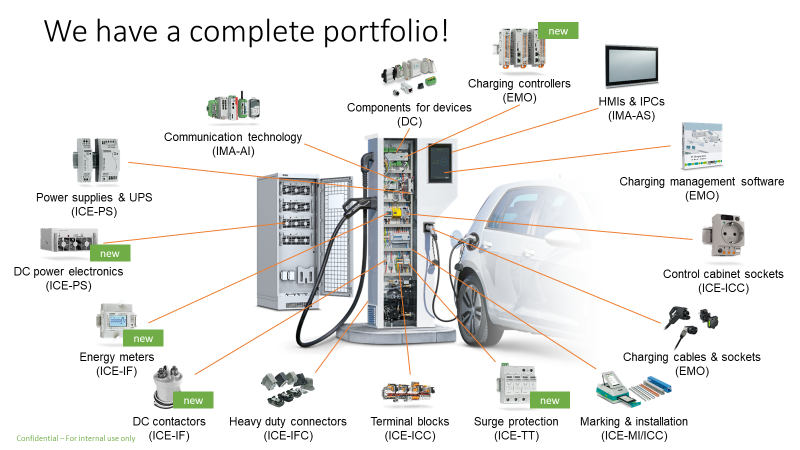
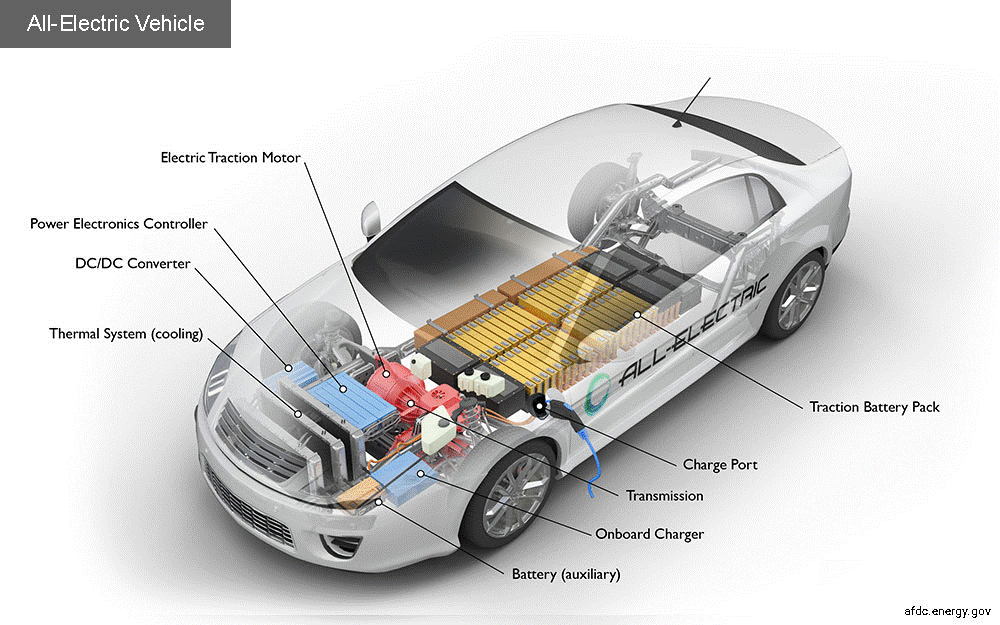
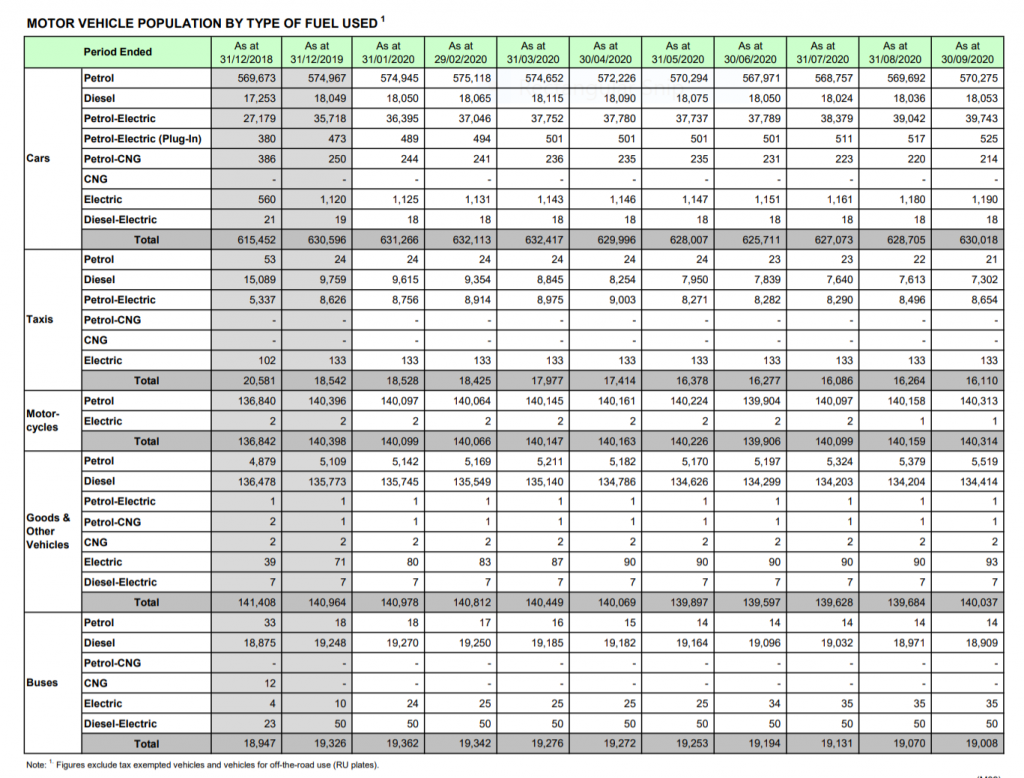
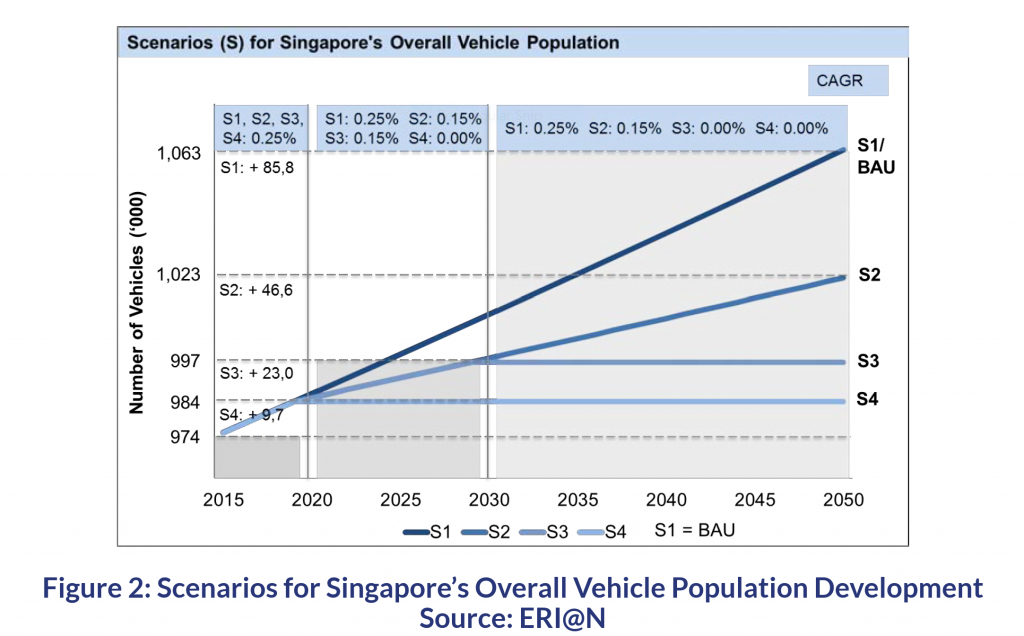
Much has been said about “Decarbonization of Transportation” and to greener Electric Vehicles (EV).
But in a small country like Singapore, is it difficult to achieve such goals?
It is almost a monumental task to convert a certain percentage of our present Internal Combustion Engines (ICE) Vehicles to EVs.
Let’s do a comparison with a similarly populated European country that has successfully converted to EVs in the last 5 years.
Norway Total Population – 5,421,241 as of 2020
Total Vehicle population – 2.8 Million of all types
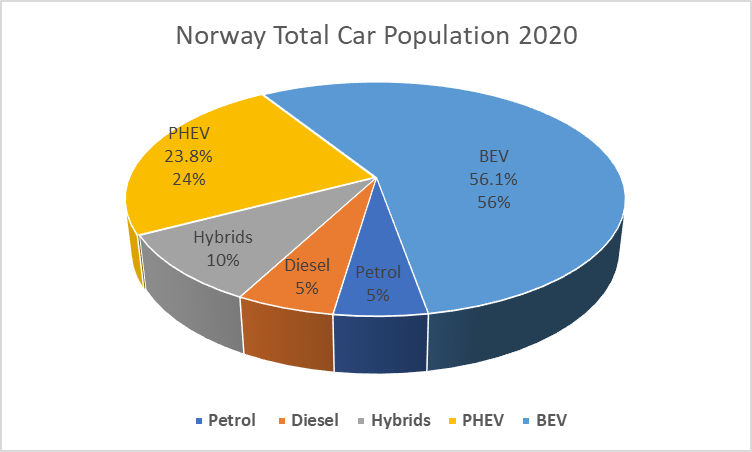
When was EV Introduced in Norway?
In 2007, Oslo started the conversion to EV by installing 400 charging points from 2008-2011 in the City as a try-out for the switch to de-carbonization from ICE Vehicles. By 2011 it was deemed a success and that started the move away from Fossil Fuel transportation. It took them 13 years for this change to happen.
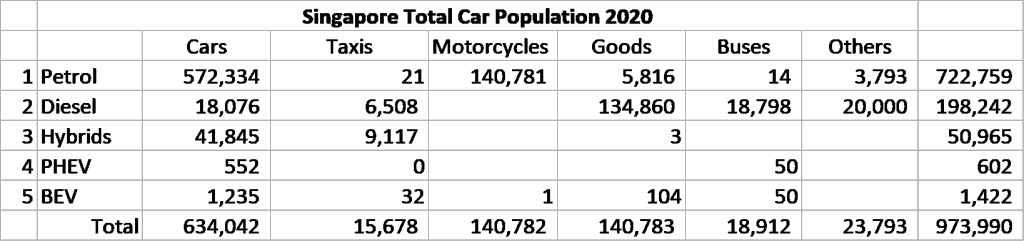
Singapore Total Population – 5,690,000 as of 2020
Total Vehicle population of 973,990 of all types
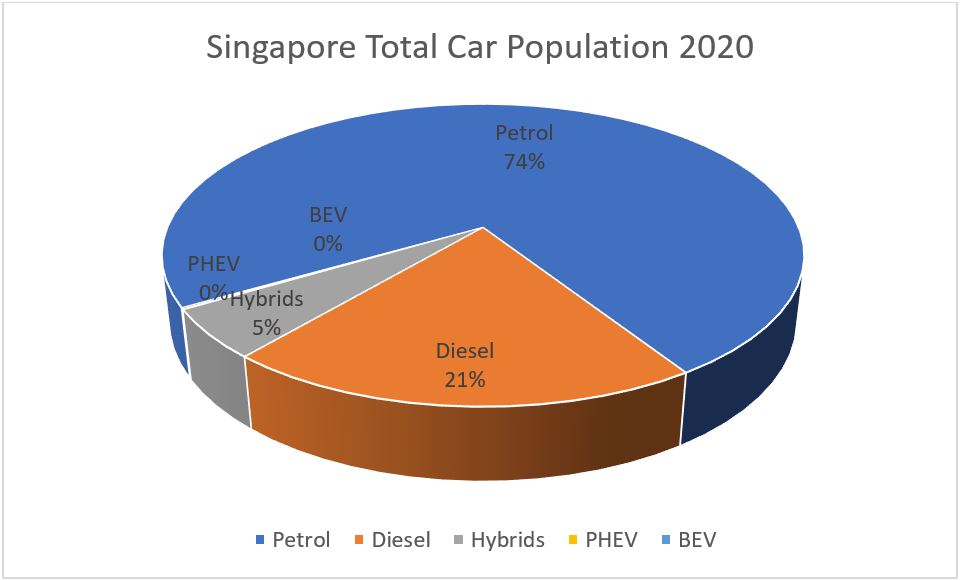
Between the 2 countries the Energy Consumption in terms of Gigawatt/hour per Quarter estimates
Norway – 13.067 GW per Quarter
Singapore – 12.6 GW per Quarter.
Majority of Energy supplied in Norway is from Hydro-electric Plants (65%) Bio Gas (25%) and (10%) Solar, whereas in Singapore, it is mostly from Bio Diesel Generation (75%) and Solar (25%).
With the above statistics in mind, let’s look at the possible solutions for Clean Energy Generation for EV Vehicles.
This time we focus on Off Grid AC and DC Charging for less dependency on Fossil fuel generation and Renewable energy.
The system requirements for OFF Grid Charging
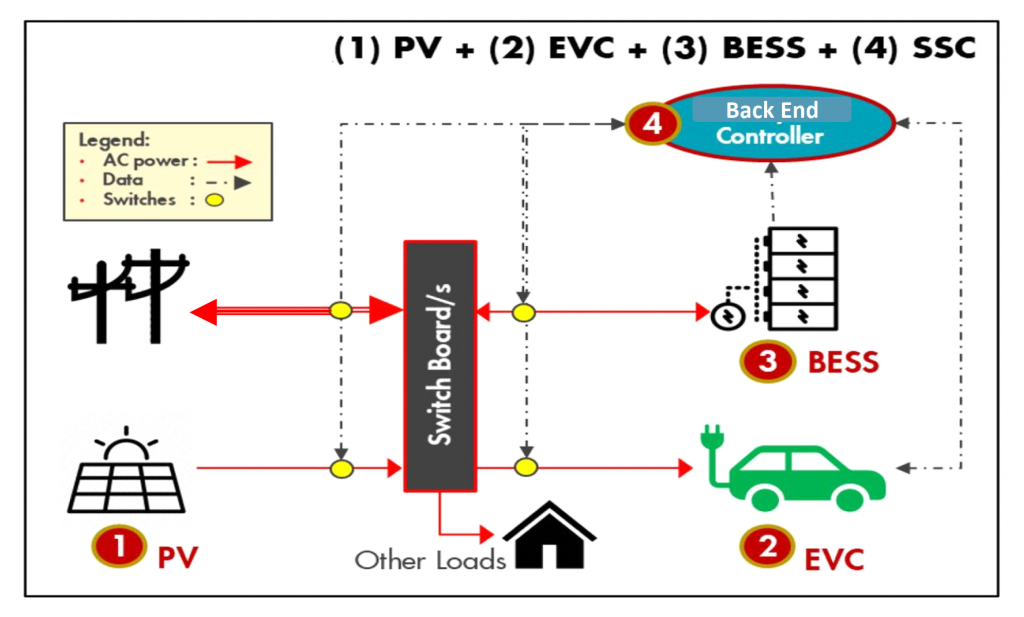
Here you have the basic Solutions block for an Off Grid System:
- PV Solutions that is connected to Main Switch board management system
- EVC – EV Chargers of AC or DC types
- BESS – Battery Energy Storage in DC (Lithium Ion or Vanadium Reflow Battery)
- Back End Controller to Gateway or for EV Charging Data
- Optional connection to Grid as backup to charging the BESS should the PV system have insufficient supply of power to BESS.
- Other loads to Motor or Pumps for infrastructure if the above is a micro grid system used in remote locations.
The above can be used with AC EV “Slow Chargers”, or if It’s connected to a bigger Solar Farm source that can connect to a 1.0MW -1.5 MW BESS to DC Fast Chargers of 60KW to 150KW.
OFF GRID AC Car Park Chargers Solutions

15/100KWh BESS connected to 2 AC chargers dispensing 7Kwh EV Charging Power
We have components for the following solutions:-
- EV charger solutions that can take 220VAC at 32 Amps Single phase to give 7Kwh AC charging. The Parking lot size caters for 2 AC Chargers.
- Power conversion rectifiers that can convert DC to AC from the BESS to AC EV Charger.
- Solar Combiner boxes from Phoenix Contact to Convert DC direct to BESS.
The solution can be connected to the back-end controller via Modbus and then to our Gateway for communication with backend.
OFF GRID DC Fast Charger Solutions
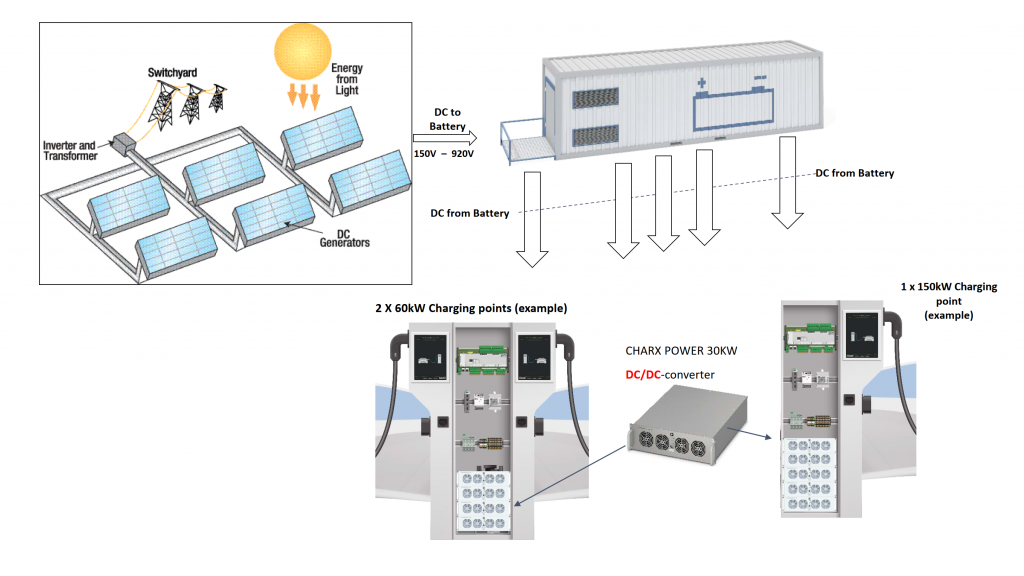
Solar Farm Generating 0.5mW connected to a BESS of 0.5MW to 1.5MW + 2 DC fast Chargers
Here in this DC Fast Charger solution, we have.
- Solar Combiners boxes to connect to BESS.
- BESS will have DC to DC rectifier blocks to stabilize the power output to the DC EV Chargers.
- Our DC Chargers will have all our “CHARX” products from HMIs to Charge controllers
DC to DC rectifiers to generate output power in DC at 60 -150Kw to EV Cars.